What is this?
International Political Economy (IPE),
or Global Political Economy
interdisciplinary analyses ultimately concerned with the ways in which political entities (states, institutions, or individuals, etc.) shape how economic activiy effect systems, and the inverse, the effect that economic interactions have upon political structures.
Traditional Approaches
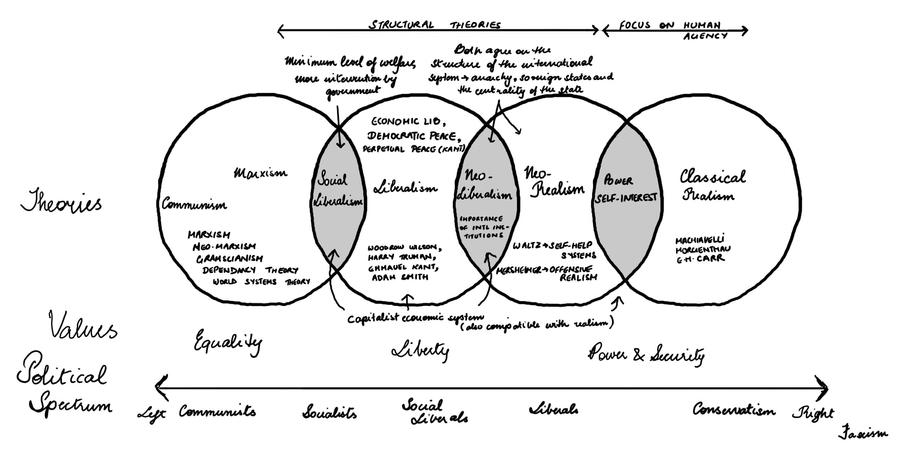
Liberal - freedom for private powers at the expense of public power/ government; markets, free from the distortions caused by government controls and regulation, will harmonise demand and supply of resources resulting in the best possible outcome for the majority
Realist (or "nationalist") - power of free markets to deliver favourable outcomes which are generally obtained with moderately strong public power exerting some regulatory control
Marxist - robust application of strong public power can check innate tendencies for private power to benefit elites at the expense of the majority
Constructivist - economic interaction is not value-free, economic and political identities along with material interests are key determinants of economic action
Databases
-
Ciao: Columbia International Affairs Online This link opens in a new windowCoverage: varies.
Articles and papers relating to International Affairs. -
EconLit This link opens in a new windowCoverage: 1969 - current
- Covers over 400 economics periodicals. -
NBER working paper series This link opens in a new windowNational Bureau of Economic Research
Coverage: November 1994 - current
- working papers focus on empirical research:
development of new statistical measures
effects of public policy on U.S. economy
and estimating quantitative models of economic behavior
More Databases
-
GreenFILE This link opens in a new windowCoverage: varies
- Scholarly and popular articles, government documents and reports
- dealing with the interaction between humans and the environment. -
Historical Abstracts This link opens in a new windowCoverage: 1967 - current
- World history (for the USA and Canada see: America, History and Life database) -
JSTOR This link opens in a new windowCoverage: late 1800's - most recent 0-10 years
- Scholarly periodicals
- Some titles exclude current issues (full text embargo) -
Project Muse Scholarly Journals Online This link opens in a new windowCoverage: varies
- Scholarly titles from John Hopkins University
- note: we do not subscribe to all titles -
Social Sciences Abstracts With Full Text This link opens in a new windowCoverage: 1983 - current
- International, English-language periodicals
- Sociology, anthropology, geography, economics, political science, and law
- Broader coverage than SocIndex.
Quick Reference
- Dictionary of Economics (Oxford)
- New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics
- Countries of the World and Their Leaders Yearbook
- World Factbook (CIA)
Chronological History of United States Foreign Relations
Reference E183.7 .B745 2003
- Political Handbook of the World
Reference JF37.P6 2011
Data sources
-
AidDataA comprehensive resource for students and professors researching foreign aid and international development.
-
World Bank DataData from over 200 countries; economics, health, energy, debt, infrastructure, development, poverty, labor, and social issues.
-
United Nations DataData areas for countries and topics: gender, health, human development, trade, tourism, information communications technology, energy, education, and crime.
-
International Monetary FundTime series data on IMF lending, exchange rates and other economic and financial indicators.
-
International Data Base (IDB)Tabular data (downloadable) for countries and regions as well as demographic indicators, population pyramids and source information for countries. Maintained by the US Census Bureau.
Agreements
-
World Treaty IndexDatabase spanning the 20th century. Indexes and provides citations to sources for full texts of multilateral and bilateral treaties.